Chemoradiation therapy (CRT) prior to surgery is increasingly the standard of care for locally advanced oesophageal cancer. Radiation therapy is important for local tumour control; however, tumour resistance to radiation is a substantial clinical problem. The mechanism(s) of radioresistance are still poorly understood, however, mounting evidence supports a role for microRNA (miRNA) in modulating key cellular pathways mediating response to radiation. Global miRNA profiling of an established isogenic model of radioresistance in oesophageal adenocarcinoma demonstrated a significant downregulation of miR-31 in radioresistant cells, both basally and in response to radiation. Ectopic re-expression of miR-31 significantly re-sensitised radioresistant cells to radiation. miR-31 was demonstrated to alter the expression of 13 genes involved in DNA repair, which is a critical cellular defence against radiation-induced DNA damage. In oesophageal tumours, miR-31 expression was significantly reduced in patients demonstrating poor histomorphologic response to neoadjuvant CRT, whilst expression of the miR-31-regulated DNA repair genes was significantly increased. Our data suggest a possible mechanism for resistance to CRT, potentially via enhanced DNA repair. This study demonstrates, for the first time, a role for miR-31 in modulating radioresistance and highlights the need for further study investigating the potential role of miR-31 as both a predictive marker of response and a novel therapeutic agent with which to enhance the efficacy of radiation therapy.
Niamh Lynam-Lennon, John V Reynolds, Laure Marignol, Orla M Sheils, Graham P Pidgeon and Stephen G Maher
Download Paper
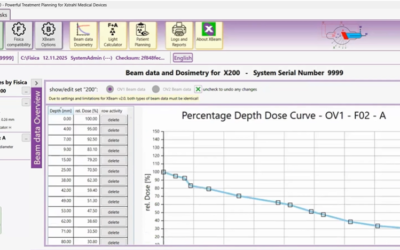
XBeam V2: FDA-Approved Treatment Planning Software
The Fastest, Safest Way to Plan Superficial & Orthovoltage Treatment XBeam V2 is the revolutionary, FDA 510(k)-cleared dose planning software designed to automate planning, eliminate risk, and seamlessly integrates with the Concerto system, Xstrahl’s...