Xstrahl in Action
The efficacy and side effects of radiotherapy (RT) depend on parameters like dose and the volume of irradiated tissue. RT induces modulations of the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) that are dependent on the dose. Low dose RT (LDRT, i.e., single doses of 0.5–2 Gy) has been shown to promote immune infiltration into the tumor. In this article, researchers from the Institut Gustave Roussy hypothesize that partial tumor irradiation combining the immunostimulatory/non-lethal properties of LDRT with cell killing/shrinkage properties of high dose RT (HDRT) within the same tumor mass could enhance anti-tumor responses when combined with immunomodulators.
Publication
Non-homogenous intratumor ionizing radiation doses synergize with PD1 and CXCR2 blockade
Authors
Paul Bergeron, Morgane Dos Santos, Lisa Sitterle, Georges Tarlet, Jeremy Lavigne, Winchygn Liu, Marine Gerbé de Thoré, Céline Clémenson, et al.
Key Findings
-
This research utilizes SARRP’s targeting accuracy to direct a low dose-RT field and a second high dose-RT field within the same tumor.
-
By triggering several features of systemic anti-tumor immunity, IR has been demonstrated to induce anti-tumor responses in lesions outside of the irradiation field. This phenomenon, called “abscopal effect”, although a rare outcome, has encouraged multiple efforts into harnessing the local and systemic effects of RT.
-
The combination of high and low irradiation doses within the same tumor mass and anti-PD1 are effective against murine colorectal and breast tumors. Experimental murine tumor models that allowed researchers to perform partial tumor irradiation with millimetric precision.
Figure 1. Irradiation setup. (a) Irradiation setting; the proton beam angled at 15° to the vertical (created with BioRender.com). (b) Dose plan in MuriPlan. Frontal view of RT planning and delivery to the cardiac apex at a dose of 40 Gy with a 5-mm diameter circular collimator angled at 15° to the horizontal. Purple and orange areas indicate the unirradiated and irradiated cardiac areas, respectively. (c) Timeline of experiments conducted in this study. (d) phosphorylated form of histone H2AX immunofluorescence staining in optimal cutting temperature-frozen FLASH proton RT or standard (conventional) proton RT-treated cardiac sections. The red dotted circle outlines the irradiated area. Scale bar, 1 mm. Abbreviation: RT = radiation therapy.
The Value of SARRP
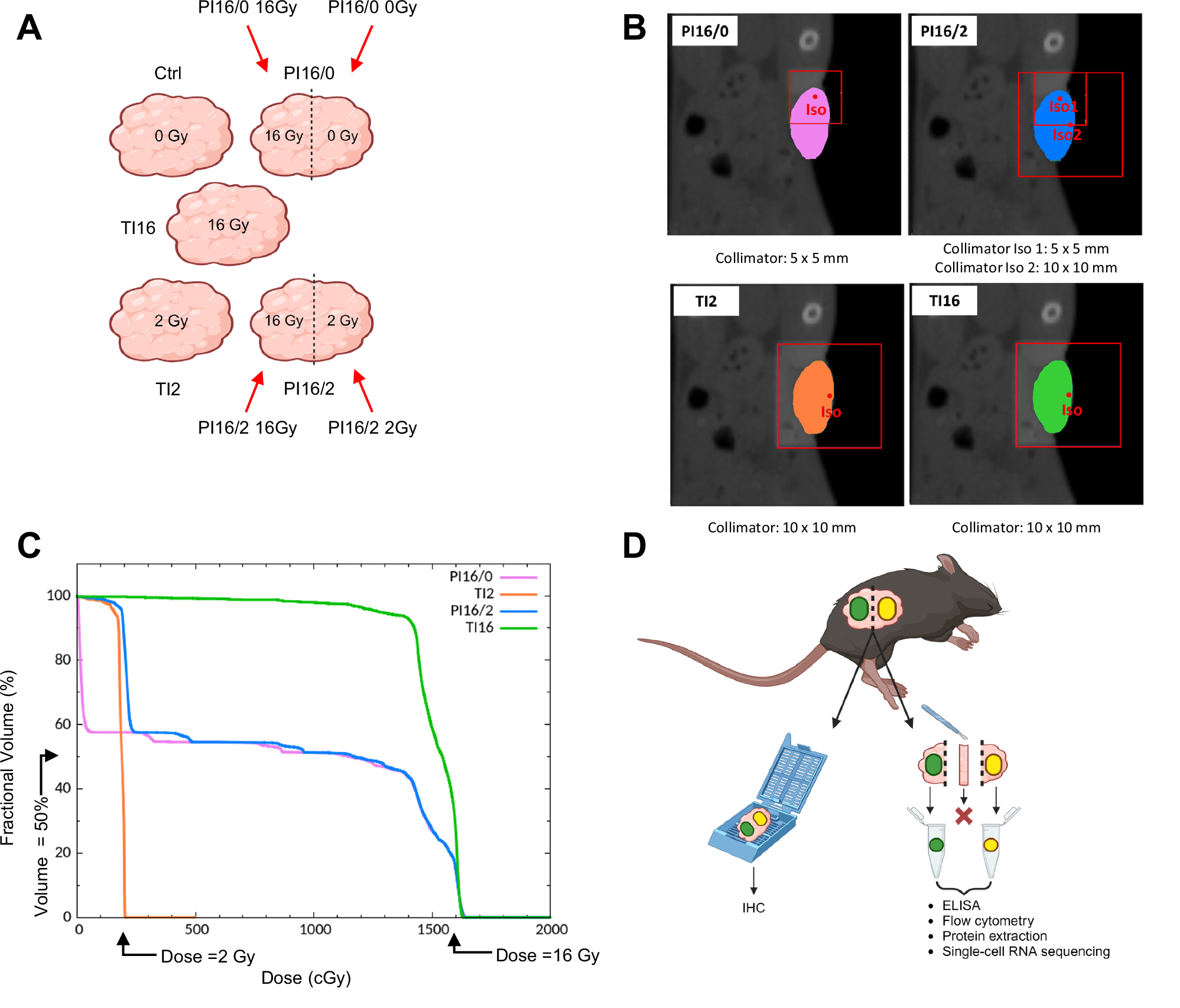
Total and partial tumor irradiations were performed using Small Animal Radiation Research Platform (SARRP). As depicted in the schematic diagram in Fig. 1A, we performed irradiations of the whole tumor volume (total irradiation, TI) at high dose (16 Gy, TI16) or low dose (2 Gy, TI2), or irradiations of 50% of the tumor volume (partial irradiation, PI) at 16 Gy (PI16/0), and a combination of 50% of tumor volume irradiated at 16 Gy with the other 50% irradiated at 2 Gy (PI16/2). The techniques used to perform PI, including the combination of high and low doses (segmentations shown in Fig. 1B), showed optimal dose distributions (Fig. 1C).