Xstrahl in Action
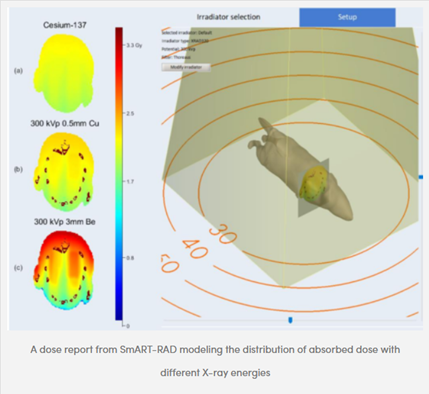
This paper describes the use and dosimetric validation of a newly developed Monte Carlo (MC) tool, SmART-RAD, to simulate the X-ray field in a range of standard commercial X-ray cabinet irradiators used for preclinical irradiations. Comparisons are made between simulated and experimentally determined dose distributions for a range of configurations to assess the potential use of this tool in determining dose distributions through samples, based on more readily available air-kerma calibration point measurements.
Published on behalf of Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine by IOP Publishing Ltd
Publication
Dosimetric Validation of SmART-RAD for X-ray Cabinet Radiobiology Irradiators
Authors
Mark A Hill, Nick Staut, James M Thompson and Frank Verhaegen
Key Findings
- Simulations gave very good dosimetric agreement with measured depth dose distributions in phantoms containing both water and bone equivalent materials, and good agreement with measured 3D dose distributions
- Good spatial and dosimetric agreement between simulated and measured dose distributions was obtained when using beam-shaping shielding.
- The MC simulations provided by SmART-RAD provide a useful tool to go from a limited number of dosimetry measurements to detailed 3D dose distributions through a non-homogeneous irradiated sample.
- The use of such a tool can improve reproducibility and dosimetry reporting in preclinical radiobiological research.
- This enables an improvement in the accuracy of delivery and reporting of relevant doses, and potentially can be used to retrospectively analyse experimental studies for comparisons between experiments and laboratories.
- SmART-RAD may also be an aid to support the current switch from Cs irradiators to kV X-ray irradiators.
The Value of Xstrahl Cabinet Irradiators
X-ray irradiations were performed using Xstrahl cabinet irradiators – performed at three different conditions along with calculated half value layers.