Xstrahl in Action
A recent study investigated reduced risk of damage to nearby organs during the treatment of ocular tumours. using our Small Animal Radiation Research Platform (SARRP).
Publication
Orthovoltage X-ray Minibeam Radiation Therapy for the Treatment of Ocular Tumours—An In Silico Evaluation
Authors
Tim Schneider, Denis Malaise, Frédéric Pouzoulet and Yolanda Prezado
Key Findings
- Radiotherapeutic treatments of ocular tumours are often challenging due to nearby organs at risk and the high doses required to treat radioresistant cancers such as uveal melanomas.
- Minibeam radiation therapy (MBRT) is an innovative treatment approach based on spatial fractionation of the dose and sub-millimetre beam sizes that has been shown to improve normal tissue sparing while maintaining high tumour control.
- Monte Carlo simulations were performed to evaluate MBRT with orthovoltage X-rays as a cost-effective treatment alternative for ocular tumours.
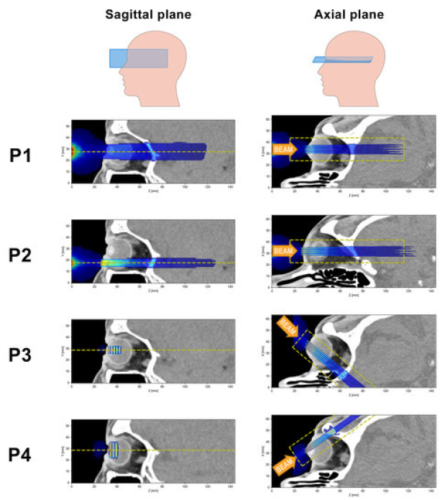
Illustration of the four different irradiation positions (P1–P4): For each row, the left and right panels show sagittal and axial sections, respectively, of the same dose distribution, while the orange arrows indicate the beam direction. The dashed yellow lines in the left panels indicate the position of the dose slices, while the dashed yellow rectangles in the right panels outline the region within the slices that were considered in the dose analysis.
The Value of SARRP
This reveals that MBRT, a feature of SARRP, has the potential to increase normal tissue sparing and provide tumour control comparable or even superior to that of conventional RT.